Ring Network Deployment for Base Station Solution
Cell Site, also known as Base Station, is an important part of modern mobile communication networks. It provides wireless signal reception and transmission services for mobile phone users, tablet users, etc., allowing users to access the mobile communication network at any time and any place to realize functions such as communication, Internet access, and voice calls.
The construction and deployment of Base Station can expand the coverage of mobile communication networks and improve signal quality. Through the transmission and reception of signals by Base Station, the network can be fully covered, signal blind spots can be reduced, and communication quality can be improved.
The main purpose of Base Station is transmission. The RRU (Remote Radio Unit) on the tower is used for wireless signal transmission and reception. It collects wireless signals and converts them into optical signals through BBU (Baseband Unit). Optical signals are transmitted through Fiber Optic Cable to thousands of miles away, even tens of thousands of miles away, and even across countries. If you want to know how signal data is transmitted, you need to first understand the classification of communication base stations. The following is an introduction to the classification of base stations:
- Macro Site
The newly built Base Station room cabinet has a device called PTN, and the Fiber Optic Cable will be connected to the PTN. The old base station also has a PTN device. The PTN device of the old Base Station is connected to the PTN device of the new Base Station through the Fiber Optic Cable. This is the simplest form of Base Station interconnection. Both the old and new base stations have PTN. From the transmission perspective, these two Base Stations are called Macro Sites. That is, the definition of Macro Site is that the station with PTN transmission equipment is called Macro Site.
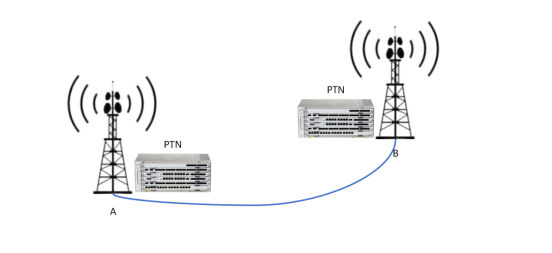
- Remote Communication Base Station System
The Base Station does not have PTN equipment. If this Base Station needs to carry out business, the wireless signal of this Base Station needs to be collected and processed by the BBU equipment, converted into an optical signal and sent to the Base Station installed with the PTN equipment, so that the signal can be transmitted thousands of miles away. Therefore, a Fiber Optic Cable is required between the BBU and PTN, which is specially used for connecting the BBU and PTN and transmitting wireless signals. Then the Base Station without PTN equipment is connected to the Base Station with PTN equipment installed nearest to the Base Station through Fiber Optic Cable. This Base Station is called Remote Communication Base Station System, and transmits the received wireless signal to the PTN of another Base Station through optical fiber.
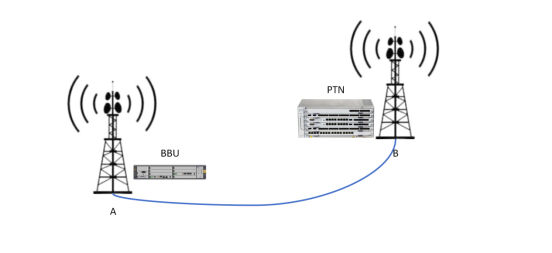
- Indoor Distributed Antenna System (DAS)
DAS can actually be classified as Remote Communication Base Station System. If the signal in this building is not good. The external base station signal cannot be transmitted into the building, or the signal is relatively weak, and there are many wireless signal devices in the building, and one base station cannot carry so many signal transmissions. The telecommunications Company adds an antenna on each floor of the building, or every few dozen meters on each floor. Antennas are divided into: Omnidirectional Antenna, Directional Antenna, Panel Antenna, Ceiling Antenna, Flat Antenna, Miniature Antenna, Small Cell Antenna. This is the Indoor Distributed Antenna System. The indoor distributed antennas on each floor will eventually converge on the BBU device in the vertical shaft of the building. The BBU is then connected to the PTN device of the external base station through Fiber Optic Cable for data transmission. Therefore, it is somewhat similar to the Remote Communication Base Station System, but the usage scenarios are different. The Remote Communication Base Station System we often talk about is the kind of large iron tower, or the pole on the building. Indoor distribution stations are just indoor antennas with more antennas. There may be dozens or hundreds of antennas in a building.

I believe that everyone has a clearer understanding of the classification of base stations, so
What are the benefits of base station ring networking?
First of all, in order to build base stations for convenience, maintainability, and safety, base station construction needs to be built according to the ring networking structure. As shown in the figure, there are 4 Macro Sites (A, B, C, D) with PTN equipment installed, and a ring connection is formed through Fiber Optic Cable. During construction, the Fiber Optic Cable between base stations B and C was dug up, but this will not affect signal transmission, because the base station signal transmission of the ring network connection is bidirectional, and B can transmit the signal to C through A-D. The final signal will be sent to the Aggregation Data Center, and the Aggregation Data Center will transmit the data to the Aggregation Data Center farther away to achieve cross-city data transmission.
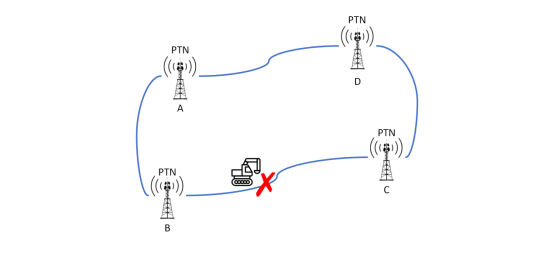
How to build a new base station in a ring network?
- Construction Survey
Base stations are used for signal data transmission. Regardless of the application scenario, Fiber Optic Cable must be used to connect base stations. Before construction, the telecommunications company will conduct a project survey to determine whether it is through poles, walls, direct burial, or overhead.
- Formulate Physical Ring and Logical Ring
Telecommunications company experts will formulate Physical Ring and Logical Ring. Physical Ring refers to the actual deployment environment of Fiber Optic Cable, and Logical Ring refers to the logic of PTN data transmission. Logical Ring needs to be implemented on the basis of Physical Ring, and it is determined whether Physical Ring is implemented in the principle of proximity.
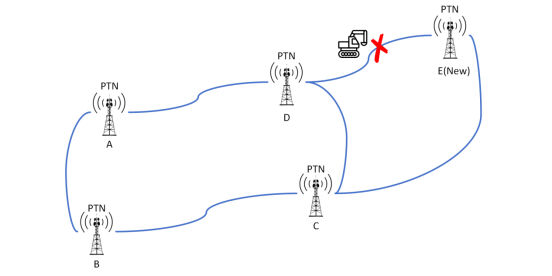
- Risks of Base Station Branch
As shown in the figure, there are currently 4 Macro Sites that are deployed in a ring, and a new base station needs to be built. The first step of the site construction plan is to find out which base stations are in the surrounding area and find the nearest base station. The second step is to check whether the PTN port capacity in the station is sufficient. If not, you can choose to expand the capacity. The third step is to lay Fiber Optic Cable to connect the base station.
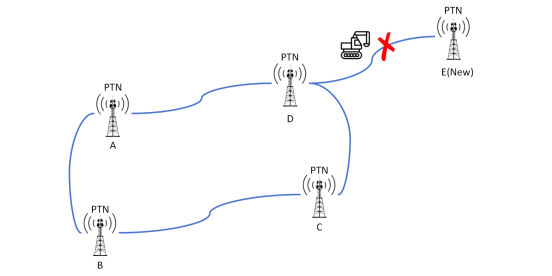
At this point, the newly built base station belongs to a branch in the ring network of these 4 Macro Sites. There is a great risk in the Base Station Branch. If the Fiber Optic Cable is broken, this base station will have the risk of Station Drop. When users make calls near this base station, they may find that the mobile phone signal is full, but the call cannot be made. The full signal represents the signal connected to the base station antenna. The RRU and BBU have processed the signal and transmitted the data to the PTN. Since the Fiber Optic Cable is broken, the PTN transmission data cannot be delivered to the next base station, and the data cannot enter the Aggregation Data Center, and the signal data cannot be sent to the target location until the Fiber Optic Cable is re-welded.
Therefore, in order to avoid the above situation, the branch base station of the ring base station needs to be changed to join the ring network structure, so it is necessary to connect the two closest base stations in the ring networking base station through 2 Fiber Optic Cables.
Conclusion:
Base station ring networking is a technical Solution that connects base stations through a ring topology to improve network redundancy, reliability and fault tolerance. The base station ring networking solution can provide high reliability and high efficiency services for the communication network through redundant design, fast recovery mechanism, intelligent management and other measures.







