Solution
- Building A, Republic International Business Plaza, No. 3699 Gonghexin Road, Jing'an District, Shanghai
- +86-21-59175887
- market@soctfiber.com
- 86-17321363317
- 86-13341796231
Comprehensive Guide to Fiber Optic Patch Cord Solutions
1. Table of Contents
1.1 Introduction to Fiber Optic Patch Cords
1.2 Types of Fiber Optic Patch Cords
- Single-Mode vs. Multi-Mode
- Connector Types
- Cable Configurations
- Common Fiber Cable Types for Patch Cord Assemblies
- Fiber Optic Type
3. Technical Specifications
- Insertion Loss and Return Loss
- Durability and Flexibility
- Operating Temperature Range
4. Applications of Fiber Optic Patch Cords
- Telecommunications
- Data Centers
- Broadcasting
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
2. Introduction to Fiber Optic Patch Cords
Fiber optic patch cords are essential components in modern communication networks, facilitating the connection between various devices and ensuring efficient data transmission. These cables, capped with connectors at both ends, enable quick and reliable connections within telecommunication equipment, data centers, and other high-speed network environments.
SoctFiber offers high-quality fiber optic patch cords with customizable packaging, reliable lead times, and logistics services optimized for smooth customs clearance.
3. Types of Fiber Optic Patch Cords
3.1 Single-Mode vs. Multi-Mode
Fiber optic patch cords are primarily categorized based on the type of optical fiber used:
- Single-Mode Fiber (SMF): Designed for long-distance data transmission, SMF cables have a small core diameter (typically 9µm) that allows light to travel straight down the fiber, minimizing signal attenuation and dispersion.
- Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF): Suited for shorter distances, MMF cables have larger core diameters (50µm or 62.5µm), permitting multiple light modes to propagate. This design is ideal for high-bandwidth applications within limited ranges.

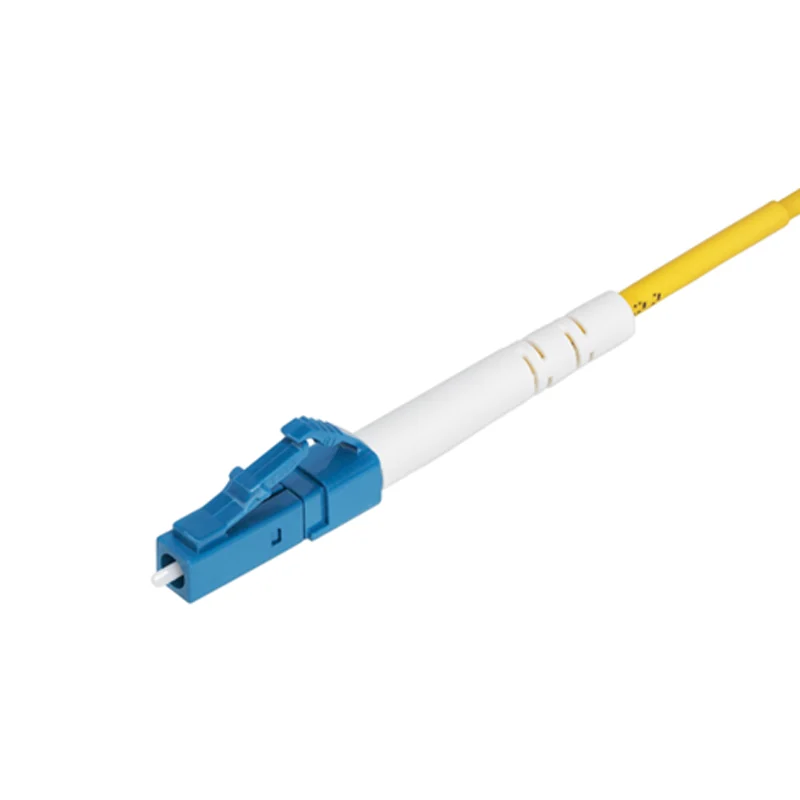
3.2 Connector Types
The performance and compatibility of fiber optic patch cords heavily depend on the connectors used. Common connector types include:
| Pictures | Connector Type | Description |
 | LC | Small form factor; widely used in high-density applications like data centers. |
 | SC | Standard square-shaped connector with a push-pull mechanism; highly durable and easy to use. |
 | ST | Bayonet-style connector commonly used in legacy networks and industrial environments. |
 | FC | Screw-on connector; provides a stable connection ideal for high-vibration environments. |
 | E2000 | Features a spring-loaded protective cap for excellent performance and dust protection. |
 | MTP/MPO | High-density connector used for parallel optical interconnects, supporting 12/24/48 fiber ribbons. |
 | MU | Smaller than SC connectors, used in high-density environments. |
 | DIN | Threaded metal connector, typically used in industrial or specialty applications. |
3.3 Cable Configurations
Fiber optic patch cords come in various configurations to meet specific networking requirements:
- Simplex: Consists of a single fiber, suitable for one-way data transmission.
- Duplex: Comprises two fibers, enabling simultaneous bi-directional communication.
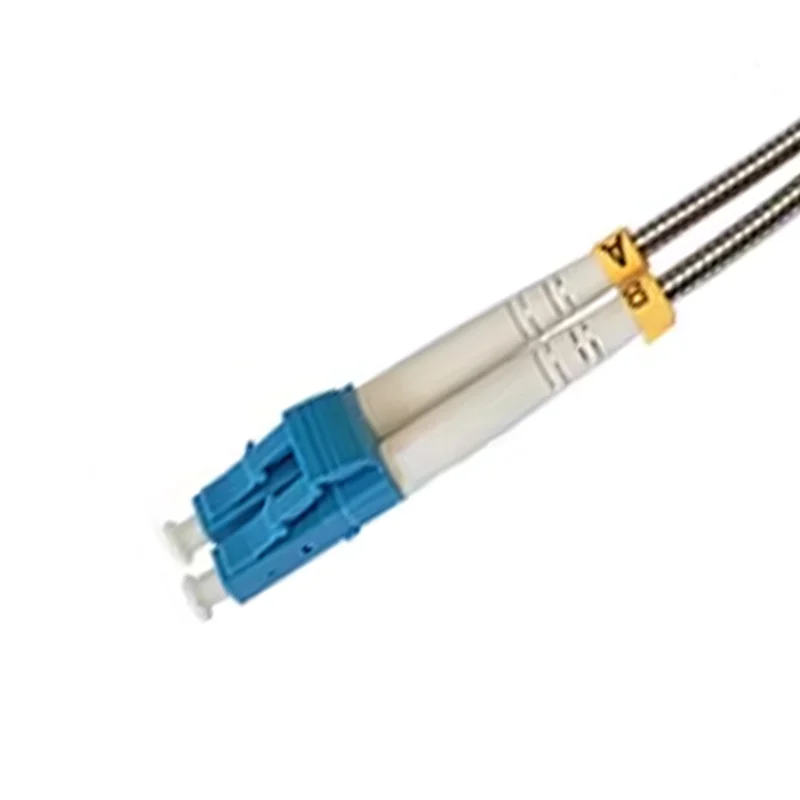
- Armored: Features a protective layer to withstand physical stress and prevent damage, ideal for harsh environments.
- Bend-Insensitive: Designed to maintain performance even when bent or twisted, reducing signal loss in tight installations.
 Simplex |  Duplex |
 Armored |  Bend-Insensitive |
3.4 Common Fiber Cable Types for Patch Cord Assemblies
In the selection of fiber optic patch cord solutions, it’s essential to understand the various types of fiber optic cables commonly used for different environments and applications. Each type is designed to meet specific installation needs and operational requirements:
| Pictures | Cable Type | Description |
 | Indoor Single-Core Cable | Ideal for point-to-point connections inside buildings; simple and compact. |
 | Indoor Duplex Cable | Contains two fibers for bi-directional data transmission; often used in LANs. |
 | Indoor Multi-Core Bundle Cable | Houses multiple fibers tightly bundled; suitable for high-density environments. |
 | Indoor Multi-Core Branch Cable | Features individual jacketed fibers; ideal for complex internal wiring setups. |
 | Indoor Multi-Core Mini Cable | Smaller in diameter, supports high-density cabling in limited spaces. |
 | Spiral Armored Cable | Offers robust mechanical protection; resists crushing and rodent damage. |
 | FTTH Drop Cable | Used for fiber-to-the-home applications; easy to install and terminate. |
 | Remote Base Station Cable | Designed for telecom base stations; supports long-distance and rugged setups. |
 | Military Tactical Cable | Ruggedized and mobile; resistant to environmental extremes and physical abuse. |
 | Outdoor Waterproof Pigtail Cable | Withstands moisture and UV exposure; used in harsh or outdoor environments. |
3.5 Fiber Optic Type
Choosing the correct fiber optic type is also essential to performance. Based on transmission mode and distance, the following fiber types are widely used:
| Fiber Type | Core Diameter | Typical Application |
| SM (Single Mode) | 9µm | Long-distance communication (>10km), high bandwidth. |
| OM1 | 62.5µm | Short-range legacy systems, supports up to 1Gbps. |
| OM2 | 50µm | Better performance than OM1, up to 10Gbps over short distances. |
| OM3 | 50µm (laser optimized) | High-speed LANs, supports 10Gbps up to 300m. |
| OM4 | 50µm (enhanced) | Data centers, up to 100Gbps over 150m. |
| OM5 | 50µm (wideband) | Supports emerging SWDM applications, optimized for 40G/100G. |
4. Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical parameters of fiber optic patch cords is crucial for optimal network performance.
4.1 Insertion Loss and Return Loss
- Insertion Loss: Represents the signal power loss due to the insertion of a connector or cable. High-quality patch cords typically exhibit insertion loss values ≤0.3dB, ensuring minimal signal degradation.
- Return Loss: Measures the amount of light reflected back toward the source. Superior patch cords achieve return loss values of ≥50dB, indicating efficient signal transmission with minimal reflections.
4.2 Durability and Flexibility
High-quality patch cords are constructed with robust materials, such as aramid yarns, to enhance strength and flexibility. This design ensures the cables can withstand repeated bending and physical stress without compromising performance.
4.3 Operating Temperature Range
Fiber optic patch cords are engineered to function effectively across a broad temperature spectrum, typically from -10°C to +60°C. This versatility makes them suitable for various indoor and outdoor applications.
5. Applications of Fiber Optic Patch Cords
- Telecommunications:In the telecommunications sector, fiber optic patch cords are pivotal in connecting network switches, routers, and other equipment, facilitating high-speed data transfer over extensive distances.
- Data Centers:Data centers rely on fiber optic patch cords to interconnect servers, storage systems, and networking hardware, ensuring rapid and reliable data exchange critical for cloud computing and large-scale data processing.
- Broadcasting:The broadcasting industry utilizes fiber optic patch cords to transmit high-definition audio and video signals, delivering superior quality and reducing latency in live broadcasts and studio productions.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How do I choose between single-mode and multi-mode fiber optic patch cords?
A1: The choice depends on the required transmission distance and bandwidth. Single-mode fibers are ideal for long-distance communication, while multi-mode fibers are suitable for shorter distances with high data rates.
Q2: Can I use different connector types on the same patch cord?
A2: Yes, hybrid patch cords with different connectors on each end are available to connect devices with varying interfaces.
Q3: What is the significance of insertion loss in patch cords?
A3: Lower insertion loss indicates better performance, as it means less signal power is lost during transmission.
Q4: Are armored patch cords necessary for indoor installations?
A4: Armored patch cords are recommended in environments where cables may be exposed to physical damage or require additional protection.
Q5: How should I maintain my fiber optic patch cords?
A5: Keep connectors clean, avoid sharp bends, use dust caps, manage cables neatly, and inspect regularly for damage or contamination.
Related Products
No results found.




